Exam 2 - Queen Anne Curiosity Shop and Writer's Patrol
Instructions
- Answer Questions A through G found on pages 187-189 in Chapter 3 for the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop.
- Answer Questions A through G found on pages 209-210 in Chapter 4 for the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop.
- Answer Questions A and B found on page 262 in Chapter 5 for the Writer's Patrol Case.
- Answer Questions A through E found on page 265 in Chapter 5 for the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop.
- Answer Questions A through E found on page 321 in Chapter 6 for the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop.
- Deliver a single sql file, along with a document that contains all the content from the sql file.
- Do not include the result table unless specifically directed to.
- Include at least one line of white space between answers.
Questions A-G in Chapter 3
Data
Figure 3.33: Typical Sales Data
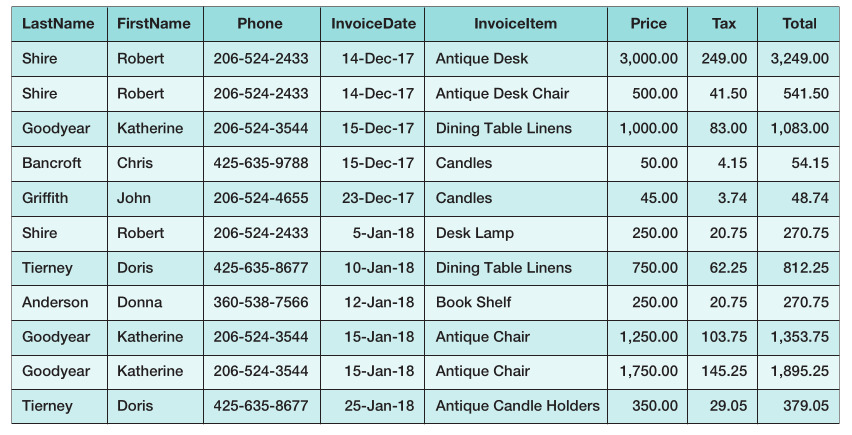
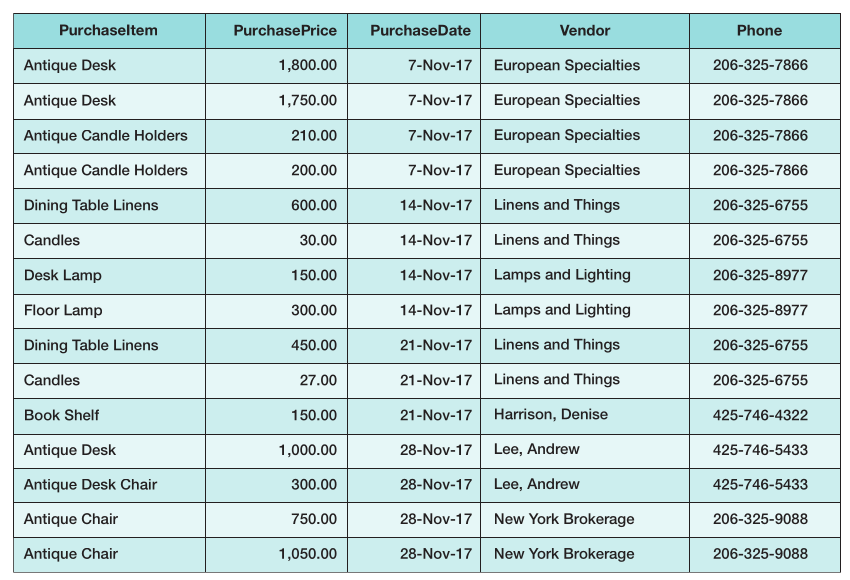
Figure 3.34: Typical Purchase Data
Questions
A.) Using these data, state assumptions about functional dependencies among the columns of data. Justify your assumptions on the basis of these sample data and also on the basis of what you know about retail sales.
B.) Given your assumptions in part A, comment on the appropriateness of the following designs:
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
- CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress)
and
SALE (InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total) - CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate)
and
SALE (InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total) - CUSTOMER (LastName, FirstName, Phone, EmailAddress, InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem)
and
SALE (InvoiceDate, InvoiceItem, Price, Tax, Total)
C.) Modify what you consider to be the best design in part B to include surrogate ID columns called CustomerID and SaleID. How does this improve the design?
D.) Modify the design in part C by breaking SALE into two relations named SALE and SALE_ITEM. Modify columns and add columns as you think necessary. How does this improve the design?
E.) Given your assumptions, comment on the appropriateness of the following designs:
- PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor, Phone)
- PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor, Phone)
- PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor, Phone)
- PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor, Phone)
- PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate)
and
VENDOR (Vendor, Phone) - PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor)
and
VENDOR (Vendor, Phone) - PURCHASE (PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, Vendor)
and
VENDOR (Vendor, Phone)
F.) Modify what you consider to be the best design in part E to include surrogate ID columns called PurchaseID and VendorID. How does this improve the design?
G.) The relations in your design from part D and part F are not connected. Modify the database design so that sales data and purchase data are related.
Questions A-G in Chapter 4
Question Information
The Queen Anne Curiosity Shop project questions in Chapter 3 asked you to create a set of relations to organize and link the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop typical sales data shown in Figure 3-33 and the typical purchase data shown in Figure 3-34. The set of relations may look similar the following, although some additional columns have been added to the CUSTOMER relation to more closely match the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop database schema shown in the Project Questions for Chapter 2:
- CUSTOMER (CustomerID, LastName, FirstName, EmailAddress, EncryptedPassword, Address, City, State, ZIP, Phone, ReferredBy)
- SALE (SaleID, CustomerID, InvoiceDate, PreTaxTotal, Tax, Total)
- SALE_ITEM (SaleID, SaleItemID, PurchaseID, SalePrice)
- PURCHASE (PurchaseID, PurchaseItem, PurchasePrice, PurchaseDate, VendorID)
- VENDOR (VendorID, Vendor, Phone)
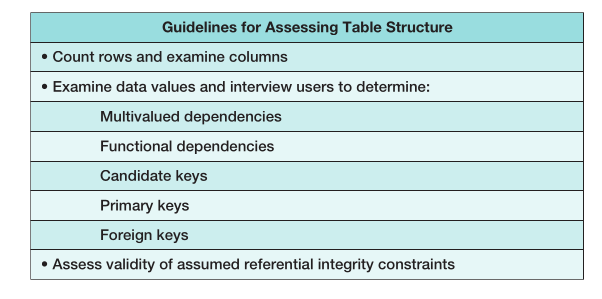
Figure 4.1: Guidelines for Assessing Table Structure
Questions
A.) Follow the procedure shown in Figure 4-1 to assess these data.
- List all functional dependencies.
- List any multivalued dependencies.
- List all candidate keys.
- List all primary keys.
- List all foreign keys.
- State any assumptions you make as you list these components.
B.) List questions you would ask the owners of the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop to verify your assumptions.
C.) If there are any multivalued dependencies, create the tables needed to eliminate these dependencies.
D.) Do these data have the multivalue, multicolumn problem? If so, how will you deal with it?
E.) Do these data have the inconsistent data problem? If so, how will you deal with it?
F.) Do these data have a null (missing) value data problem? If so, how will you deal with it?
G.) Do these data have the general-purpose remarks problem? If so, how will you deal with it?
Questions A and B in Chapter 5
Data
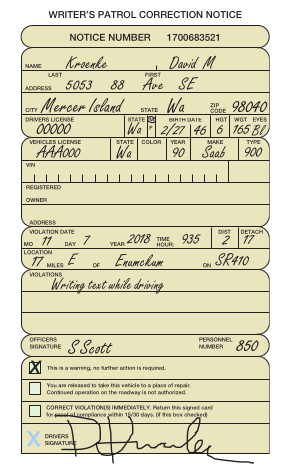
Consider the traffic citation shown below:
Figure 5.61: Writer's Patrol Correction Notice
Questions
A.) Create the entities for an E-R data model based on the traffic citation form. Use five entities, and use the data items on the form to specify identifiers and attributes for those entities. In which of these entities should you place the unique Notice Number that is the unique identifier for this notice?
B.) Complete the E-R data model by specifying relationships among the entities. Use IE Crow’s Foot E-R symbols as shown in Figure 5-8. Name the relationships, and specify the relationship types and cardinalities. Justify the decisions you make regarding minimum and maximum cardinalities, indicating which cardinalities can be inferred from data on the form and which need to be checked out with systems users.
Questions A-E in Chapter 5
Question Information
The Queen Anne Curiosity Shop wants to expand its database applications beyond the current recording of sales. The company still wants to maintain data on customers, employees, vendors, sales, and items, but it wants to (a) modify the way it handles inventory and (b) simplify the storage of customer and employee data.
Currently, each item is considered unique, which means the item must be sold as a whole, and multiple units of the item in stock must be treated as separate items in the ITEM table. The Queen Anne Curiosity Shop management wants the database modified to include an inventory system that will allow multiple units of an item to be stored under one ItemID.
The system should allow for a quantity on hand, a quantity on order, and an order due date. If the identical item is stocked by multiple vendors, the item should be orderable from any of these vendors. The SALE_ITEM table should then include Quantity and ExtendedPrice columns to allow for sales of multiple units of an item.
The Queen Anne Curiosity Shop management has noticed that some of the fields in CUSTOMER and EMPLOYEE store similar data. Under the current system, when an employee buys something at the store, his or her data has to be reentered into the CUSTOMER table. The managers would like to have the CUSTOMER and EMPLOYEE tables redesigned using subtypes.
Questions
A.) Draw an E-R data model for the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop database schema shown in Chapter 3’s The Queen Anne Curiosity Shop Project Questions. Use the IE Crow’s Foot E-R model for your E-R diagrams. Justify the decisions you make regarding minimum and maximum cardinalities.
B.) Extend and modify the E-R data model by adding only the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop’s inventory system requirements. Use the IE Crow’s Foot E-R model for your E-R diagrams. Create appropriate identifiers and attributes for each entity. Justify the decisions you make regarding minimum and maximum cardinalities.
C.) Extend and modify the E-R data model by adding only the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop’s need for more efficient storage of CUSTOMER and EMPLOYEE data. Use the IE Crow’s Foot E-R model for your E-R diagrams. Create appropriate identifiers and attributes for each entity. Justify the decisions you make regarding minimum and maximum cardinalities.
D.) Combine the E-R data models from parts B and C to meet all of the Queen Anne Curiosity Shop’s new requirements, making additional modifications as needed. Use the IE Crow’s Foot E-R model for your E-R diagrams.
E.) Describe how you would go about validating your data model in part D.
Questions A-E in Chapter 6
NOTE: Use the questions from the end of Chapter 5.
A.) Convert this data model to a database design. Specify tables, primary keys, and foreign keys. Using Figure 6-43 as a guide, specify column properties.
B.) Describe how you have represented weak entities, if any exist.
C.) Describe how you have represented supertype and subtype entities, if any exist.
D.) Create a visual representation of your database design as a Crow’s Foot E-R diagram similar to the one in Figure 6-39.
E.) Document your minimum cardinality enforcement using referential integrity actions for required parents, if any, and the form in Figure 6-29(b) for required children, if any.